The Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park stands as a remarkable testament to India's rich and complex historical tapestry. Nestled in the Panchmahal district of Gujarat, this extraordinary site weaves together layers of cultural, religious, and architectural narratives that span millennia. From prehistoric settlements to the dynamic interactions between Hindu and Muslim civilizations, the landscape tells a story of continuous human habitation and cultural transformation.
Archaeological evidence reveals that the region has been inhabited since the chalcolithic period, with human presence dating back thousands of years. The city's formal establishment is attributed to Vanraj Chavda, a prominent king of the Chavda Dynasty, who founded Champaner in the eighth century. Named after his friend and general Champa, the settlement would become a pivotal location in the region's intricate historical narrative.
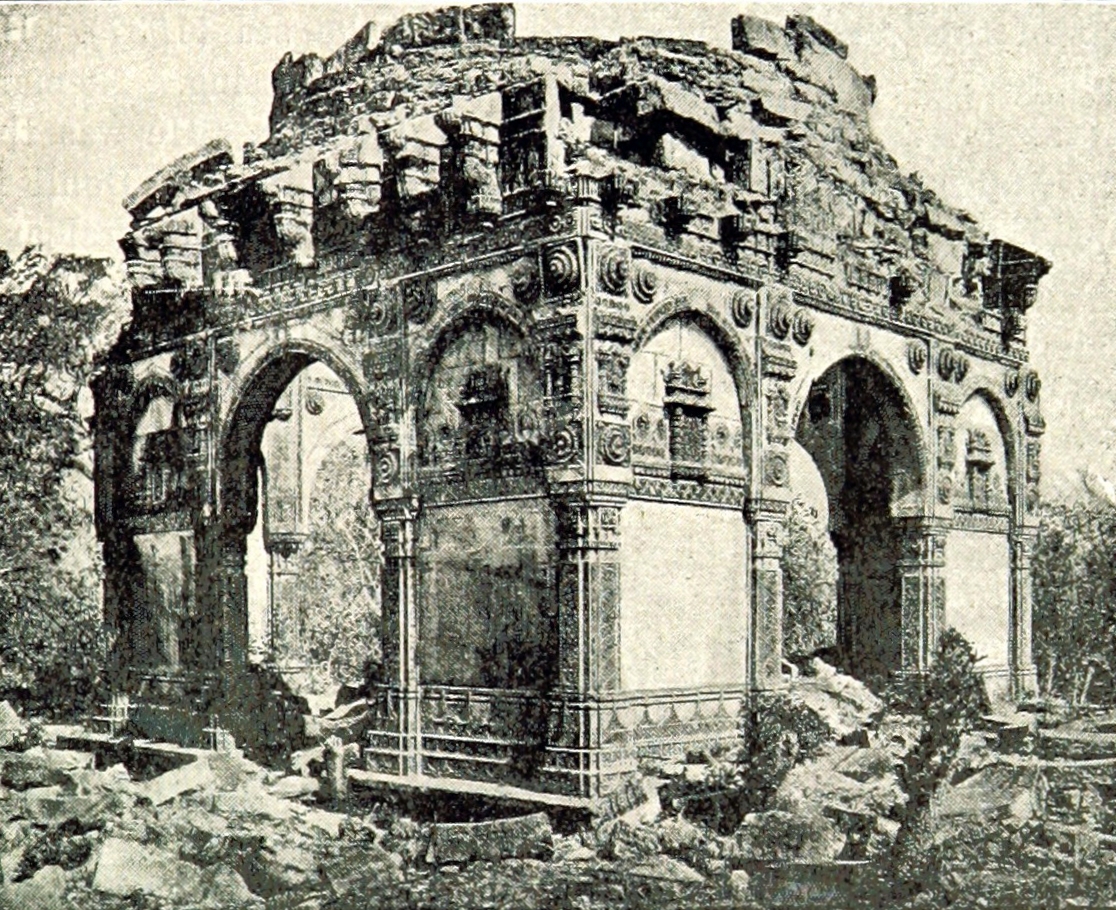
The site's most significant period emerged during the late 15th century when Sultan Mehmud Begda transformed Champaner into the capital of Gujarat. This era marked a profound cultural synthesis, where Islamic architectural traditions merged seamlessly with existing Hindu and Jain cultural practices. The urban landscape became a canvas of architectural brilliance, showcasing mosques, temples, and palaces that reflected the nuanced cultural interactions of the time.
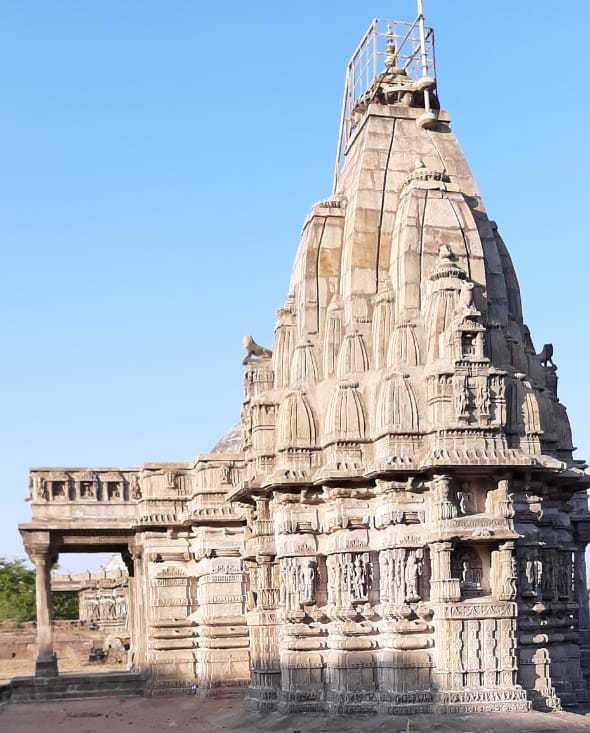
Religious diversity has always been a hallmark of Champaner-Pavagadh. The Kalika Mata Temple, perched atop Pavagadh Hill, exemplifies this spiritual richness. According to local legend, the temple is built where the goddess Kalika's right toe is said to have fallen, making it a site of immense religious significance. This sacred space continues to draw Hindu pilgrims throughout the year, maintaining its spiritual vitality across generations.
The architectural heritage of Champaner-Pavagadh represents a unique blend of pre-Mughal Islamic and indigenous architectural styles. The Jama Masjid stands as a prime example, incorporating design elements that reflect both Muslim and Hindu aesthetic sensibilities. Constructed primarily from local sandstone and marble, these structures demonstrate the sophisticated building techniques of their time, showcasing the region's technological and artistic prowess.
Historical transitions were often marked by conflict and conquest. The Rajput warriors, known for their resilience, fought numerous battles to maintain control of the region. The city's fortunes shifted dramatically with the Mughal invasion in the 16th century, which ultimately led to its gradual decline. Despite these tumultuous periods, Champaner-Pavagadh preserved its cultural essence, becoming a living museum of historical interactions.
In recognition of its extraordinary cultural significance, UNESCO inscribed Champaner-Pavagadh as a World Heritage Site in 2004. This designation was the result of collaborative efforts by the Baroda Heritage Trust and the Archaeological Survey of India, who worked tirelessly to preserve and promote the site's historical integrity. Today, it represents not just a historical location, but a dynamic cultural landscape that continues to inspire and educate visitors from around the world.
Modern conservation efforts have transformed Champaner-Pavagadh into a premier cultural destination. Pilgrims, historians, and tourists are drawn to its multifaceted heritage, exploring the intricate monuments that bear witness to centuries of human creativity and spiritual expression. As a living testament to India's rich cultural diversity, the site continues to bridge past and present, inviting visitors to explore the complex layers of human civilization that have unfolded in this remarkable landscape.